Today we are talking about the top four use cases for streaming data integration. If you’re not familiar with streaming data integration, please check out our channel for a deeper dive into the technology. In this 7-minute video, let’s focus on the use cases.
Use Case #1 Cloud Adoption – Online Database Migration
The first one is cloud adoption – specifically online database migration. When you have your legacy database and you want to move it to the cloud and modernize your data infrastructure, if it’s a critical database, you don’t want to experience downtime. The streaming data integration solution helps with that. When you’re doing an initial load from the legacy system to the cloud, the Change Data Capture (CDC) feature captures all the new transactions happening in this database as it’s happening. Once this database is loaded and ready, all the changes that happened in the legacy database can be applied in the cloud. During the migration, your legacy system is open for transactions – you don’t have to pause it.
While the migration is happening, CDC helps you to keep these two databases continuously in-sync by moving the real-time data between the systems. Because the system is open to transactions, there is no business interruption. And if this technology is designed for both validating the delivery and checkpointing the systems, you will also not experience any data loss.
Because this cloud database has production data, is open to transactions, and is continuously updated, you can take your time to test it before you move your users. So you have basically unlimited testing time, which helps you minimize your risks during such a major transition. Once the system is completely in-sync and you have checked it and tested it, you can point your applications and run your cloud database.
This is a single switch-over scenario. But streaming data integration gives you the ability to move the data bi-directionally. You can have both systems open to transactions. Once you test this, you can run some of your users in the cloud and some of you users in the legacy database.
All the changes happening with these users can be moved between databases, synchronized so that they’re constantly in-sync. You can gradually move your users to the cloud database to further minimize your risk. Phased migration is a very popular use case, especially for mission-critical systems that cannot tolerate risk and downtime.
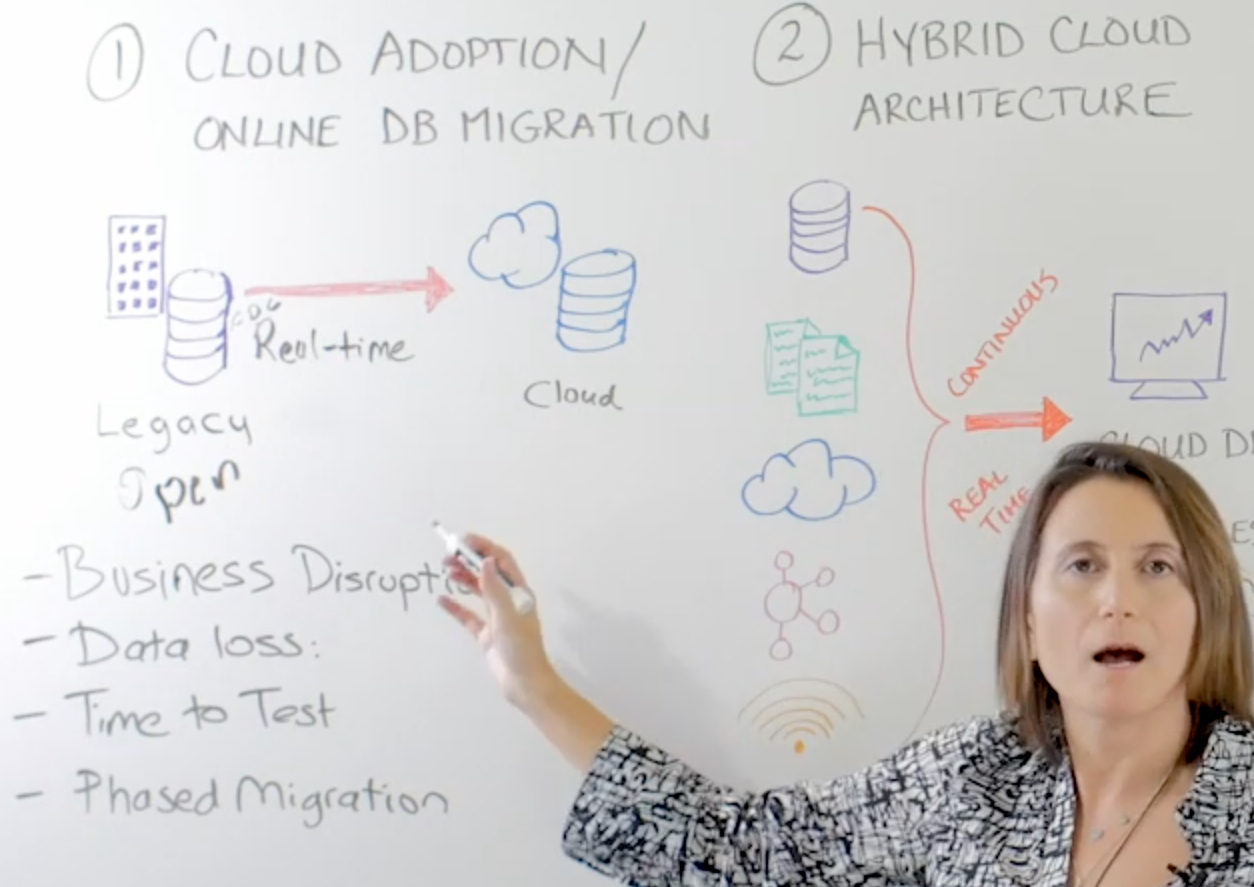
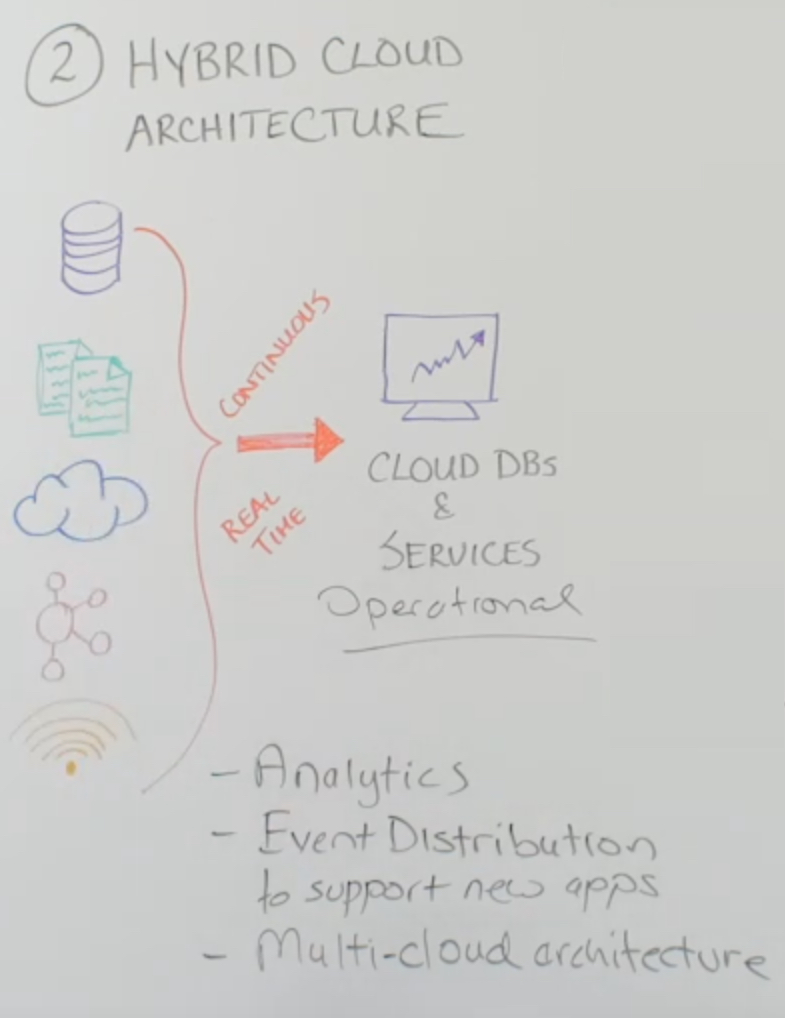
Once you’re in the cloud and you have a hybrid cloud architecture, you need to maintain it. You need to connect it with the rest of your enterprise. It needs to be a natural extension of your data center. Continuous real-time data moment with streaming data integration allows you to have your cloud databases and services as part of your data center.
The important thing is that these workloads in the cloud can be operational workloads because there’s fresh information (ie, continuously updated information) available. Your databases, your machine data, your log files, your other cloud sources, messaging systems, and sensors can move continuously to enable operational workloads.
What do we see in hybrid cloud architectures? Heavy use of cloud analytics solutions. If you want operational reporting or operational intelligence, you want comprehensive data delivered continuously so that you can trust that’s up-to-date, and gain operational intelligence from your analytics solutions.
You can also connect your data sources with the messaging systems in the cloud to support event distribution for your new apps that you’re running in the cloud so that they are completely part of your data center. If you’re adopting multi-cloud solutions, you can again connect your new cloud systems with existing cloud systems, or send data to multiple cloud destinations.
A third use case is real-time modern applications. Cloud is a big trend right now, but not everything is necessarily in the cloud. You can have modern applications on-premises. So, if you’re building any real-time app and modern new system that needs timely information, you need to have continuous real-time data pipelines. Streaming data integration enables you run real-time apps with real-time data.
Use Case #4 Hot Cache
Last, but not least, when you have an in-memory data grid to help with your data retrieval performance, you need to make sure it is continuously up-to-date so that you can rely on that data – it’s something that users can depend on. If the source system is updated, but your cache is not updated, it can create business problems. By continuously moving real-time data using CDC technology, streaming data integration helps you to keep your data grid up-to-date. It can serve as your hot cache to support your business with fresh data.
To learn more about streaming data integration use cases, please visit our Products section, schedule a demo with a Striim expert, or download the Striim platform to get started.