Oracle
Oracle is a relational database management system developed by Oracle Corporation.
Coverage for Oracle
Category | Details |
|---|---|
Supported versions |
|
Supported validation methods |
|
Supported data types in Oracle
Character | Datatypes |
|---|---|
Character |
|
Numeric |
|
Date & Time |
|
Rowid |
|
Boolean data |
|
Note
Per Oracle documentation, the NUMBER datatype behaves as floating-point numeric if precision/scale is not specified by the user. Validata formats it with five digits of precision in scientific notation.
Connecting Validata to Oracle Database
Validata connects to Oracle Database using a connection profile that specifies your Oracle server endpoint and authentication credentials. For information about connection profiles, see Managing connection profiles.
Validata uses the Oracle JDBC Thin Driver to connect to Oracle Database and supports username and password authentication.
Prerequisites
Before creating an Oracle connection profile, ensure the following requirements are met:
An Oracle Database instance accessible from the Validata server.
Network connectivity to the Oracle listener on the configured port (default 1521, or 2484 for SSL/TLS connections).
An Oracle user account with appropriate database permissions.
The Oracle user account must have the following privileges on the schemas and tables being validated:
SELECT — Allows read access to table data.
DESCRIBE — Allows access to table metadata and schema information.
CONNECT — Allows the user to establish a database session.
Oracle connection profile parameters
When you create a connection profile for Oracle, you configure the parameters described in this section.
The following image shows the connection profile configuration for Oracle:
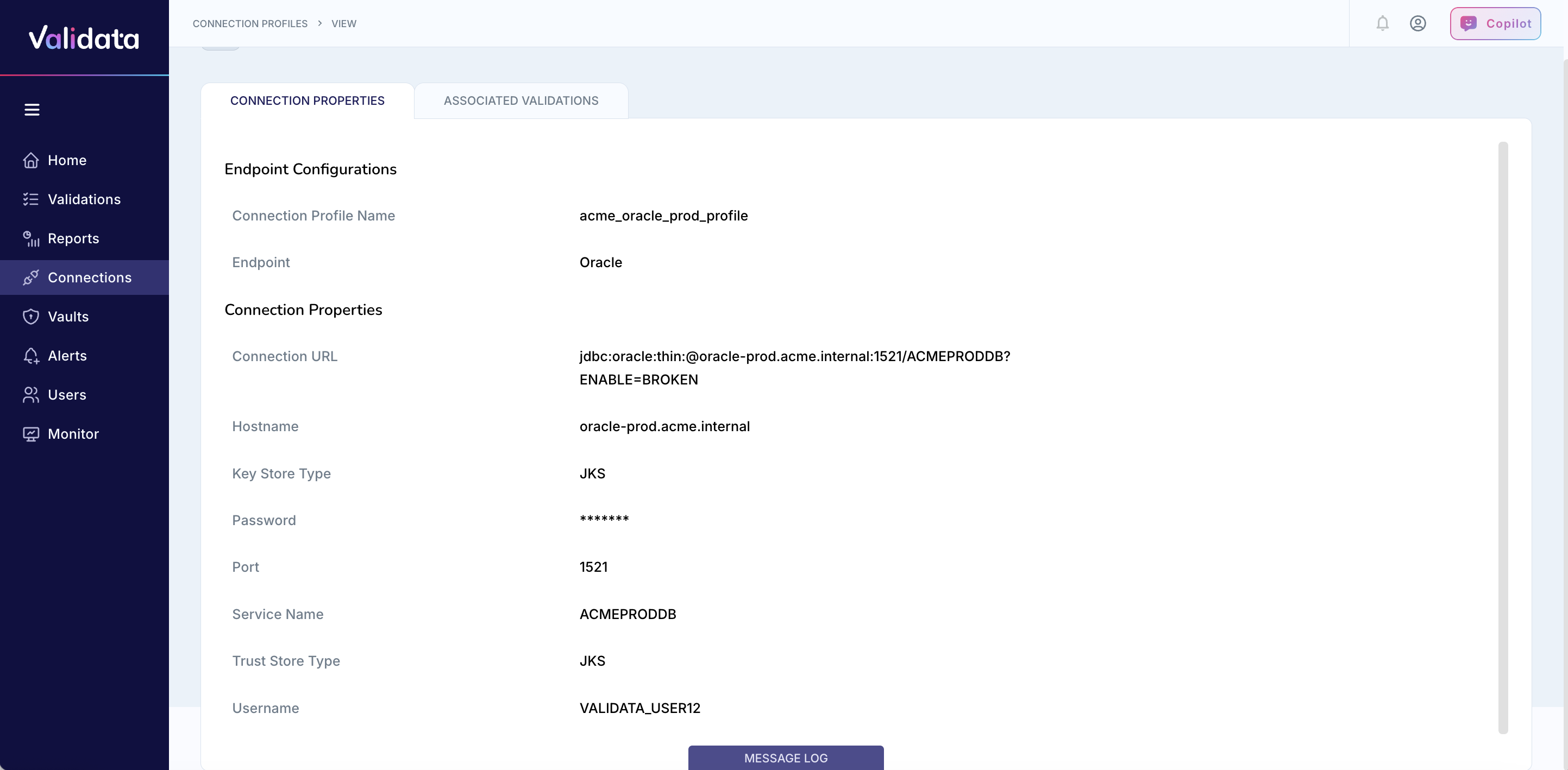
The following table describes each connection profile parameter for Oracle:
Parameter | Required | Description | Example value |
|---|---|---|---|
Connection Profile Name | Yes | A unique name that identifies this connection profile. | acme_oracle_prod_profile |
Endpoint | Yes | The external data system type. Select | Oracle |
Host Name | Yes | The hostname or IP address of the Oracle Database server. | oracle-prod.acme.internal |
Port | Yes | The Oracle listener port. The default port is 1521 for standard connections or 2484 for SSL/TLS connections. | 1521 |
Service Name | Yes | The Oracle Service Name for pluggable or non-CDB databases. Using Service Name is recommended over SID. | ACMEPRODDB |
Username | Yes | The Oracle username with SELECT, DESCRIBE, and CONNECT privileges on the target schemas. | VALIDATA_USER12 |
Password | Yes | The password for the Oracle user. Validata stores this value securely. | (stored securely) |
Connection URL (JDBC) | Yes | The JDBC connection URL for Oracle. Use the Service Name format for pluggable databases or the SSL-enabled format for secure connections. | jdbc:oracle:thin:@//oracle-prod.acme.internal:1521/ACMEPRODDB |
Configuring an Oracle connection profile
To configure an Oracle connection profile:
Set Endpoint to
Oracle.Enter the Host Name or IP address of your Oracle server.
Enter the Port number (default is 1521).
Enter the Service Name for your database.
Enter the Username and Password for authentication.
Enter the Connection URL (JDBC) with appropriate parameters.
When Validata connects to Oracle:
Validata uses the Oracle JDBC Thin Driver to connect to the target database.
The Oracle listener authenticates the connection using the provided username and password.
Once connected, Validata performs schema discovery and data comparison as part of validation runs.
JDBC connection URL formats
The JDBC connection URL specifies how Validata connects to the Oracle Database. You can use different URL formats depending on your database configuration and security requirements.
The following table describes the available JDBC connection URL formats:
Connection type | URL format | Example |
|---|---|---|
Standard (Service Name) | jdbc:oracle:thin:@//<HOST>:<PORT>/<SERVICE_NAME> | jdbc:oracle:thin:@//192.168.1.100:1521/ORCL |
Legacy (SID) | jdbc:oracle:thin:@<HOST>:<PORT>:<SID> | jdbc:oracle:thin:@192.168.1.100:1521:ORCL |
SSL-enabled | jdbc:oracle:thin:@(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcps)(HOST=<HOST>)(PORT=2484))(CONNECT_DATA=(SERVICE_NAME=<SERVICE_NAME>))) | jdbc:oracle:thin:@(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcps)(HOST=db.acme.com)(PORT=2484))(CONNECT_DATA=(SERVICE_NAME=PRODDB))) |
The following table provides guidance on selecting the appropriate connection format:
Use case | Recommended format |
|---|---|
Basic connection to Oracle instance | Standard (Service Name) |
Container or pluggable databases | Standard (Service Name) |
Legacy non-CDB databases using SID | Legacy (SID) |
Secure production environments | SSL-enabled |
Note
Use Service Name connections (@//host:port/service_name) rather than legacy SID connections (@host:port:SID) whenever possible. Service Name is required for pluggable databases and is the recommended format for all new deployments.
Best practices
Follow these recommendations when configuring Oracle connection profiles:
Use Service Name connections rather than legacy SID connections for compatibility with container and pluggable databases.
Restrict database privileges to SELECT, DESCRIBE, and CONNECT for validation users. Avoid granting broader permissions than necessary.
Store credentials securely in Oracle Wallet, a vault, or a secrets manager. Do not embed passwords in scripts or configuration files.
For production environments, enable SSL/TLS encryption on the Oracle listener and use the TCPS protocol with port 2484.
Rotate credentials periodically and enforce strong password policies for Oracle user accounts.
Ensure the Oracle listener is configured to accept connections from the Validata server's IP address.