Databricks
Databricks is a cloud-based data and AI platform that unifies data engineering, analytics, and machine learning onto a single workspace at enterprise scale.
Coverage for Databricks
Category | Details |
|---|---|
Supported versions |
|
Supported validation methods |
|
Note
When replication to Databricks uses APPEND mode to create and populate tables, you should use Custom Validation with SQL queries that produce a deduplicated, latest-record snapshot view of both the Source and Target tables. Custom Validation supports validation between a database table and a warehouse table populated in APPEND mode, as well as between two warehouse tables when one or both use APPEND-mode replication.
Supported data types in Databricks
Character | Datatypes |
|---|---|
Character |
|
Numeric |
|
Date & Time |
|
Boolean |
|
Connecting Validata to Databricks on Azure
Validata connects to Azure Databricks SQL Warehouse using a connection profile that specifies your Databricks workspace endpoint and authentication credentials. For information about connection profiles, see Managing connection profiles.
Validata supports three authentication methods for Databricks on Azure:
Personal Access Token (PAT) — Uses a Databricks-generated token for authentication. This is the simplest method and is recommended for most deployments.
Manual OAuth — Uses Azure Active Directory (AAD) client credentials and a refresh token for delegated access. This method is ideal for service-based automation or multi-user environments where PATs are not allowed.
Entra ID authentication — Redirects to the Azure portal for interactive or federated login. Use this method when SSO or MFA is enforced by your organization.
Prerequisites
Before creating a Databricks connection profile, ensure the following requirements are met:
An Azure Databricks workspace with a SQL Warehouse endpoint.
Network connectivity to the Databricks control plane on port 443.
Authentication credentials based on your chosen method (PAT, OAuth credentials, or Entra ID access).
The user account or service principal must have the following permissions on the tables being validated:
SELECT — Allows read access to table data.
DESCRIBE — Allows access to table metadata and schema information.
Databricks connection profile parameters
When you create a connection profile for Databricks, you configure the parameters described in this section. Some parameters are required for all authentication methods, while others apply only to specific methods.
The following image shows the connection profile configuration for Databricks:
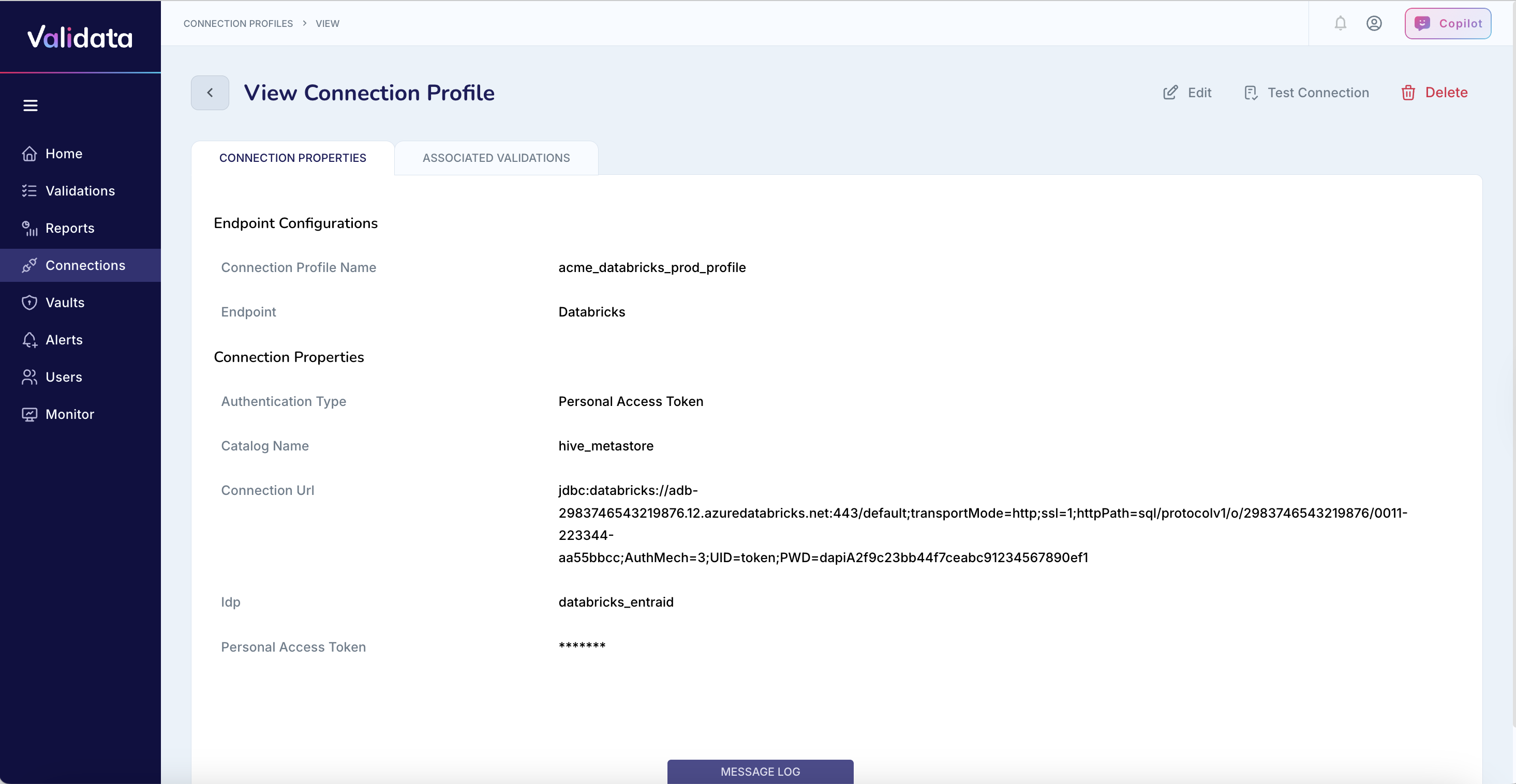
The following table describes each connection profile parameter for Databricks:
Parameter | Required | Description | Example value |
|---|---|---|---|
Connection Profile Name | Yes | A unique name that identifies this connection profile. | acme_databricks_prod_profile |
Endpoint | Yes | The external data system type. Select | Databricks |
Warehouse Link (Host) | Yes | The URL of the Azure Databricks SQL Warehouse endpoint. | https://adb-2983746543219876.12.azuredatabricks.net/ |
Authentication Type | Yes | The authentication method to use. Options are Personal Access Token (PAT), Manual OAuth, or Entra ID. | Personal Access Token (PAT) |
Catalog Name | Yes | The Databricks catalog to query for data validation. | hive_metastore |
Personal Access Token | PAT only | The Databricks personal access token. Required only when using PAT authentication. Tokens typically expire after 90 days. | dapiA2f9c23bb44f7ceabc91234567890ef1 |
Client ID | OAuth only | The Azure AD application (service principal) ID. Required only when using Manual OAuth authentication. | 00000000-1111-2222-3333-444444444444 |
Client Secret | OAuth only | The secret generated in Azure AD for the application. Required only when using Manual OAuth authentication. | abcdEFGHijklMNOPqrstUVWXyz1234567890 |
Tenant ID | OAuth only | The Azure AD tenant (directory) identifier. Required only when using Manual OAuth authentication. | 11111111-2222-3333-4444-555555555555 |
Refresh Token | OAuth only | The OAuth refresh token used to renew access without reauthentication. Required only when using Manual OAuth authentication. | 1.ABCDEF1234567890abcdefg... |
Connection URL (JDBC) | Yes | The full JDBC connection URL for accessing the Databricks SQL Warehouse. Required for all authentication methods. | jdbc:databricks://adb-2983746543219876.12.azuredatabricks.net:443/default;transportMode=http;ssl=1;... |
Authenticating with a personal access token
Personal Access Token (PAT) authentication uses a Databricks-generated token to authenticate Validata with the SQL Warehouse. This is the simplest authentication method and is recommended for most deployments.
To configure authentication with a personal access token:
Set Endpoint to
Databricks.Enter your Warehouse Link (Host) URL.
Set Authentication Type to
Personal Access Token (PAT).Enter your Catalog Name.
Enter your Personal Access Token.
Enter the Connection URL (JDBC) with appropriate parameters.
The following table shows an example configuration:
Parameter | Example value |
|---|---|
Connection Profile Name | acme_databricks_pat |
Endpoint | Databricks |
Warehouse Link (Host) | https://adb-1234567890123456.99.azuredatabricks.net/ |
Authentication Type | Personal Access Token (PAT) |
Catalog Name | hive_metastore |
Personal Access Token | dapi1234567890abcdef1234567890abcd |
Connection URL (JDBC) | jdbc:databricks://adb-1234567890123456.99.azuredatabricks.net:443/default;transportMode=http;ssl=1;httpPath=sql/protocolv1/o/1234567890123456/0123-456789-testpath;AuthMech=3;UID=token;PWD=dapi1234567890abcdef1234567890abcd |
The following table describes the JDBC connection URL parameters for PAT authentication:
Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
transportMode=http | Specifies HTTP as the transport protocol. |
ssl=1 | Enables SSL/TLS encryption for secure connectivity. |
httpPath | The HTTP path to the SQL Warehouse endpoint. Obtain this value from your Databricks workspace. |
AuthMech=3 | Specifies token-based authentication. |
UID=token | The user identifier for token authentication. Use the literal value |
PWD | The personal access token value. |
Note
Personal Access Tokens typically expire after 90 days. Rotate tokens regularly and update the connection profile before expiration to avoid authentication failures.
Authenticating with manual OAuth
Manual OAuth authentication uses Azure Active Directory (AAD) application credentials and a refresh token to obtain secure, renewable access. This method is ideal for service-based automation or multi-user environments where PATs are not allowed.
To configure authentication with manual OAuth:
Set Endpoint to
Databricks.Enter your Warehouse Link (Host) URL.
Set Authentication Type to
Manual OAuth.Enter your Catalog Name.
Enter your Azure AD credentials: Client ID, Client Secret, Tenant ID, and Refresh Token.
Enter the Connection URL (JDBC) with appropriate parameters.
The following table shows an example configuration:
Parameter | Example value |
|---|---|
Connection Profile Name | acme_databricks_oauth |
Endpoint | Databricks |
Warehouse Link (Host) | https://adb-1234567890123456.99.azuredatabricks.net/ |
Authentication Type | Manual OAuth |
Catalog Name | hive_metastore |
Client ID | 00000000-1111-2222-3333-444444444444 |
Client Secret | abcdEFGHijklMNOPqrstUVWXyz1234567890 |
Tenant ID | 11111111-2222-3333-4444-555555555555 |
Refresh Token | 1.ABCDEF1234567890abcdefg... |
Connection URL (JDBC) | jdbc:databricks://adb-1234567890123456.99.azuredatabricks.net:443/default;transportMode=http;ssl=1;httpPath=sql/protocolv1/o/1234567890123456/0123-456789-testpath;AuthMech=3;UID=token;PWD=<ACCESS_TOKEN> |
Note
Replace <ACCESS_TOKEN> in the Connection URL with a valid OAuth access token generated using your refresh token. The refresh token must correspond to the same Azure tenant and Databricks workspace.
Authenticating with Entra ID
Entra ID authentication allows users to connect to Databricks using their Azure account via an interactive or federated login flow. This method redirects to the Azure portal for credential authorization and is appropriate when SSO or MFA is enforced by your organization.
To configure authentication with Entra ID:
Set Endpoint to
Databricks.Enter your Warehouse Link (Host) URL.
Set Authentication Type to
Entra ID.Enter your Catalog Name.
Enter the Connection URL (JDBC) with appropriate parameters.
Ensure proper Azure AD access permissions are configured for the user account.
The following table shows an example configuration:
Parameter | Example value |
|---|---|
Connection Profile Name | acme_databricks_entra |
Endpoint | Databricks |
Warehouse Link (Host) | https://adb-1234567890123456.99.azuredatabricks.net/ |
Authentication Type | Entra ID |
Catalog Name | hive_metastore |
Connection URL (JDBC) | jdbc:databricks://adb-1234567890123456.99.azuredatabricks.net:443/default;transportMode=http;ssl=1;httpPath=sql/protocolv1/o/1234567890123456/0123-456789-testpath;AuthMech=3;UID=token;PWD=<ACCESS_TOKEN> |
Note
Entra ID authentication requires interactive login and is not suitable for unattended or scheduled validation jobs. For automated scenarios, use Manual OAuth with refresh tokens instead.
Best practices
Follow these recommendations when configuring Databricks connection profiles:
Use HTTPS (port 443) with SSL enabled (
ssl=1) for all connections to Databricks.Store credentials securely in Azure Key Vault or another secrets management solution. Do not commit tokens or secrets to source control.
Rotate Personal Access Tokens before the 90-day expiration and update connection profiles accordingly.
For multi-tenant or automated deployments, use Manual OAuth credentials instead of PATs for improved security and lifecycle management.
Use Entra ID authentication when SSO or MFA is enforced by your organization, but only for interactive scenarios.
Grant the minimum required permissions (SELECT and DESCRIBE) on validated tables rather than broader workspace-level access.
Ensure the refresh token used for Manual OAuth corresponds to the same Azure tenant and Databricks workspace as the connection profile.
Operational considerations for Databricks
This section describes operational considerations that affect how Validata compares datasets in Databricks.
Validating tables replicated with APPEND mode
When replication to Databricks uses APPEND mode to create and populate tables, you should use Custom Validation with SQL queries that produce a deduplicated, latest-record snapshot view of both the source and target tables.
Custom Validation supports validation in the following scenarios:
Between a database table and a warehouse table populated in APPEND mode.
Between two warehouse tables when one or both use APPEND-mode replication.