BigQuery
BigQuery is a cloud-based data warehousing and analytics platform developed by Google.
Coverage for BigQuery
Category | Details |
|---|---|
Supported versions |
|
Supported validation methods |
|
Note
When replication to BigQuery uses APPEND mode to create and populate tables, you should use Custom Validation with SQL queries that produce a deduplicated, latest-record snapshot view of source and/or target tables. Custom Validation supports validation between a database table and a warehouse table populated in APPEND mode, as well as between two warehouse tables when one or both use APPEND-mode replication.
Supported data types in BigQuery
Character | Datatypes |
|---|---|
Character |
|
Numeric |
|
Date & Time |
|
Boolean |
|
Connecting Validata to Google BigQuery
Validata connects to Google BigQuery using a connection profile that specifies your Google Cloud project and authentication credentials. For information about connection profiles, see Managing connection profiles.
Validata supports two authentication methods for BigQuery:
Service account key — Uses a JSON key file for authentication. This is the simplest method for most deployments.
Connection URL (JDBC) — Uses a JDBC connection string that references the service account key. This method is ideal for automated or scripted environments.
Prerequisites
Before creating a BigQuery connection profile, ensure the following requirements are met:
A Google Cloud project containing the BigQuery datasets that Validata will access.
A service account with appropriate BigQuery permissions.
A service account key file (JSON format) downloaded and stored securely.
The service account must have the following IAM roles on the target datasets:
BigQuery Data Viewer — Allows read access to dataset contents.
BigQuery Job User — Allows execution of BigQuery jobs.
BigQuery Read Session User — Required only if using the BigQuery Storage API.
BigQuery connection profile parameters
When you create a connection profile for BigQuery, you configure the parameters described in this section. Some parameters are required, while others are optional or apply only to specific authentication methods.
The following image shows the connection profile configuration for BigQuery:
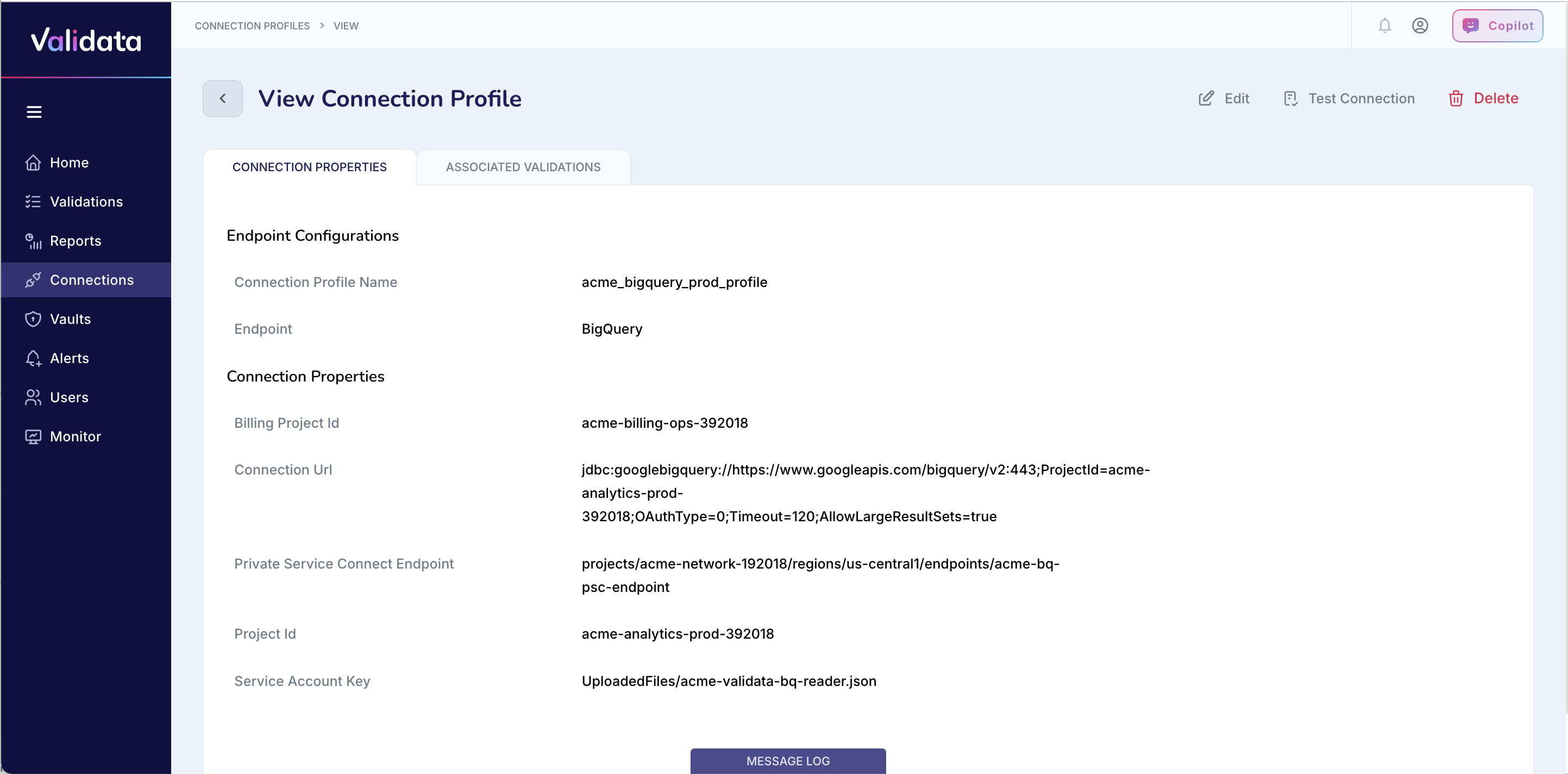
The following table describes each connection profile parameter for BigQuery:
Parameter | Required | Description | Example value |
|---|---|---|---|
Connection Profile Name | Yes | A unique name that identifies this connection profile. | acme_bigquery_prod_profile |
Endpoint Type | Yes | The data system type. Select | BigQuery |
Project ID | Yes | The Google Cloud project containing the BigQuery datasets that Validata will connect to. | acme-analytics-prod-392018 |
Billing Project ID | No | The project to bill for BigQuery query execution. If not specified, the Project ID is used for billing. | acme-billing-ops-392018 |
Service Account Key | Yes | The service account key JSON file. Upload the file or specify the file path. Required for both authentication methods. | acme-validata-bq-reader.json |
Private Service Connect Endpoint | No | The Private Service Connect (PSC) endpoint for private networking to BigQuery. Use this parameter when BigQuery is not accessible over the public internet. | projects/acme-network-192018/regions/us-central1/endpoints/acme-bq-psc-endpoint |
Connection URL | No | A JDBC URL for advanced connection parameters. Use this parameter only when authenticating with the Connection URL method. | jdbc:googlebigquery://https://www.googleapis.com/bigquery/v2:443;ProjectId=acme-analytics-prod-392018 |
Authenticating with a service account key
Service account key authentication uses a JSON key file to authenticate Validata with BigQuery. This is the simplest authentication method and is suitable for most deployments.
To configure authentication with a service account key:
Set Endpoint Type to
BigQuery.Enter your Google Cloud Project ID.
Upload your Service Account Key JSON file.
Configure optional parameters as needed (Billing Project ID, Private Service Connect Endpoint).
The following table shows an example configuration:
Parameter | Example value |
|---|---|
Connection Profile Name | acme_bigquery_prod |
Endpoint Type | BigQuery |
Project ID | acme-analytics-123456 |
Service Account Key | /opt/validata/keys/bq-service.json |
Authenticating with a connection URL (JDBC)
Connection URL authentication uses a JDBC connection string that references the service account key and includes additional connection parameters. This method provides more control over connection behavior and is ideal for automated or CI/CD environments.
To configure authentication with a connection URL:
Set Endpoint Type to
BigQuery.Enter your Google Cloud Project ID.
Upload your Service Account Key JSON file.
Enter the Connection URL with appropriate JDBC parameters.
The following table shows an example configuration:
Parameter | Example value |
|---|---|
Connection Profile Name | acme_bigquery_jdbc |
Endpoint Type | BigQuery |
Project ID | acme-analytics-123456 |
Service Account Key | /opt/validata/keys/bq-service.json |
Connection URL | jdbc:googlebigquery:AuthScheme=OAuthJWT;OAuthJWTCert=/opt/validata/keys/bq-service.json;InitiateOAuth=GETANDREFRESH;ProjectId=acme-analytics-123456;Other=KeepRawStringDataTypes=TIME;UseStorageAPI=false;AllowLargeResultSets=true |
The following table describes the JDBC connection URL parameters:
Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
AuthScheme=OAuthJWT | Specifies service account authentication using OAuth JWT. |
OAuthJWTCert | The path to the service account JSON key file. |
InitiateOAuth=GETANDREFRESH | Automatically handles OAuth token creation and refresh. |
ProjectId | The Google Cloud project where BigQuery datasets reside. |
KeepRawStringDataTypes=TIME | Keeps TIME fields as strings. This parameter is optional. |
UseStorageAPI=false | Disables the BigQuery Storage API. Set to |
AllowLargeResultSets=true | Enables handling of large query result sets. |
Best practices
Follow these recommendations when configuring BigQuery connection profiles:
Use HTTPS (port 443) for all connections to BigQuery.
Restrict file system access to the JSON key file and rotate the key periodically.
Store credentials in Google Secret Manager or another secure secrets management solution. Do not commit key files to source control.
Grant dataset-level permissions rather than project-wide roles to follow the principle of least privilege.
For shared or automated environments, use the Connection URL authentication method for easier CI/CD integration.
Reuse the same service account key for multiple validation jobs across datasets in the same project.
Operational considerations for BigQuery
This section describes operational considerations and configuration options that affect how Validata compares datasets in BigQuery.
Case sensitivity in schema names
The Validata query engine for BigQuery is case sensitive. If two schemas exist with the same name but different letter casing (for example, Sales and SALES), Validata displays them with schema 1 and schema 2 postfixes to distinguish between them.
Validating tables replicated with APPEND mode
When replication to BigQuery uses APPEND mode to create and populate tables, you should use Custom Validation with SQL queries that produce a deduplicated, latest-record snapshot view of both the source and target tables.
Custom Validation supports validation in the following scenarios:
Between a database table and a warehouse table populated in APPEND mode.
Between two warehouse tables when one or both use APPEND-mode replication.
Handling large result sets
BigQuery has default limits on result set sizes. When working with large datasets that exceed these limits, you must configure the allowLargeResultSets property in your JDBC connection URL. This property enables BigQuery to create temporary tables in the BigQuery instance to fetch extremely large result sets.
The following example shows a connection URL with the allowLargeResultSets property enabled:
jdbc:bigquery://[Host]:[Port];ProjectId=[Project];OAuthType=[OAuthType];allowLargeResultSets=true;[additional_properties]
The following table describes the allowLargeResultSets property:
Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
Property name |
|
Type | Boolean |
Default value | false |
Purpose | Enables BigQuery to handle large result sets by creating temporary tables. |
Configure this property when:
Working with large datasets.
Encountering
responseTooLargeerrors.Performing custom query validations on large tables.
Running queries that may exceed BigQuery's default result set limits.
When configuring allowLargeResultSets, consider the following:
Performance impact — Creating temporary tables may increase query execution time.
Resource usage — Temporary tables consume additional BigQuery storage resources.
Cleanup — BigQuery automatically cleans up temporary tables.
Note
Configure the allowLargeResultSets property based on actual need rather than as a default setting. Enabling this property when not required may impact performance and resource usage.