Microsoft SQL Server
SQL Server is a relational database management system developed by Microsoft Corporation.
Coverage for SQL Server
Category | Details |
|---|---|
Supported versions |
|
Supported validation methods |
|
Supported data types in SQL Server
Character | Datatypes |
|---|---|
Character |
|
Numeric |
|
Date & Time |
|
Monetary |
|
Other |
|
Connecting Validata to Microsoft SQL Server
Validata connects to Microsoft SQL Server databases using a connection profile that specifies your SQL Server instance endpoint and authentication credentials. For information about connection profiles, see Managing connection profiles.
Validata uses standard JDBC connectivity to connect to SQL Server and supports SQL authentication with username and password.
Prerequisites
Before creating a SQL Server connection profile, ensure the following requirements are met:
A Microsoft SQL Server instance accessible from the Validata server.
Network connectivity to the SQL Server instance on the configured port (default 1433).
A SQL Server login with appropriate database permissions.
SQL Server configured to allow remote connections.
The SQL Server login must have the following permissions on the databases and tables being validated:
SELECT — Allows read access to table data.
VIEW DEFINITION — Allows access to table metadata and schema information.
Ensure SQL Server allows remote connections by verifying the configuration in SQL Server Configuration Manager and checking that firewall rules permit inbound connections on the SQL Server port.
SQL Server connection profile parameters
When you create a connection profile for SQL Server, you configure the parameters described in this section.
The following image shows the connection profile configuration for SQL Server:
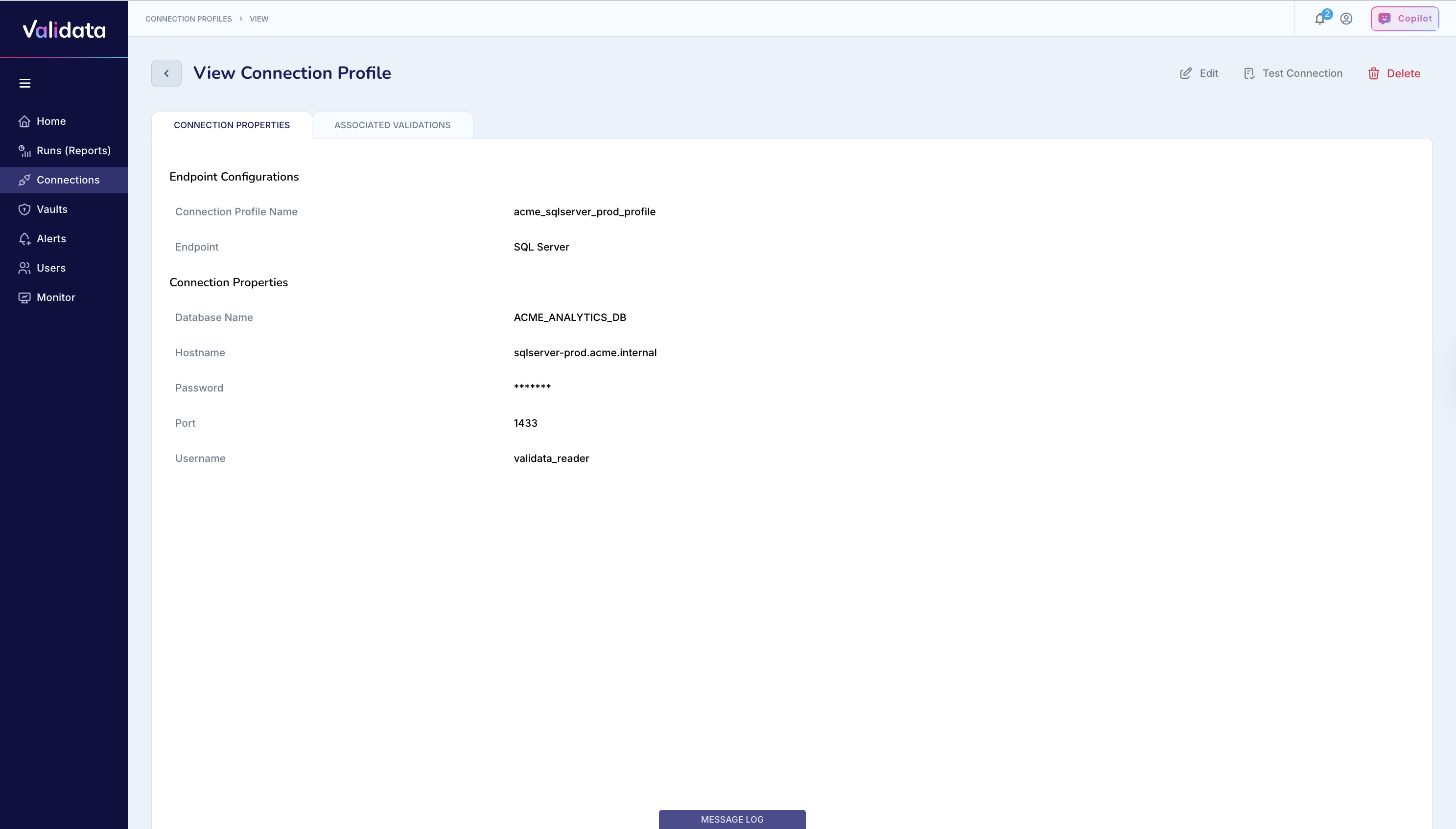
The following table describes each connection profile parameter for SQL Server:
Parameter | Required | Description | Example value |
|---|---|---|---|
Connection Profile Name | Yes | A unique name that identifies this connection profile. | acme_sqlserver_prod_profile |
Endpoint | Yes | The external data system type. Select | SQL Server |
Host Name | Yes | The hostname or IP address of the SQL Server instance. | sqlserver-prod.acme.internal |
Port | Yes | The SQL Server port. The default port is 1433. | 1433 |
Database Name | Yes | The name of the SQL Server database that Validata will validate. | ACME_ANALYTICS_DB |
Username | Yes | The SQL Server login with SELECT and VIEW DEFINITION permissions on the target database. | validata_user12 |
Password | Yes | The password for the SQL Server login. Validata stores this value securely. | (stored securely) |
Connection URL (JDBC) | Yes | The JDBC connection URL for SQL Server. You can include additional parameters for encryption, timeouts, and other connection settings. | jdbc:sqlserver://sqlserver-prod.acme.internal:1433;databaseName=ACME_ANALYTICS_DB |
Configuring a SQL Server connection profile
To configure a SQL Server connection profile:
Set Endpoint to
SQL Server.Enter the Host Name or IP address of your SQL Server instance.
Enter the Port number (default is 1433).
Enter the Database Name to connect to.
Enter the Username and Password for SQL authentication.
Enter the Connection URL (JDBC) with appropriate parameters.
JDBC connection URL formats
The JDBC connection URL specifies how Validata connects to the SQL Server instance. You can use different URL formats depending on your security and configuration requirements.
The following table describes the available JDBC connection URL formats:
Connection type | URL format | Example |
|---|---|---|
Standard | jdbc:sqlserver://<HOST>:<PORT>;databaseName=<DATABASE_NAME> | jdbc:sqlserver://192.168.1.220:1433;databaseName=VALIDATA_DB |
With encryption enabled | jdbc:sqlserver://<HOST>:<PORT>;databaseName=<DATABASE_NAME>;encrypt=true;trustServerCertificate=false | jdbc:sqlserver://sqlserver-prod.acme.internal:1433;databaseName=ACME_ANALYTICS_DB;encrypt=true;trustServerCertificate=false |
With additional parameters | jdbc:sqlserver://<HOST>:<PORT>;databaseName=<DATABASE_NAME>;encrypt=true;loginTimeout=30;applicationName=Validata | jdbc:sqlserver://sqlserver-prod.acme.internal:1433;databaseName=ACME_ANALYTICS_DB;encrypt=true;loginTimeout=30;applicationName=Validata |
The following table describes common JDBC connection URL parameters:
Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
encrypt=true | Enables TLS encryption for the connection. Required for secure data-in-transit in production environments. |
loginTimeout | The timeout value in seconds for establishing a connection. Use this parameter to avoid long waits when the server is unreachable. |
applicationName | The application name reported to SQL Server. This value appears in |
failoverPartner | The hostname of a failover partner for database mirroring or Always On availability groups. Use this parameter for high-availability configurations. |
Best practices
Follow these recommendations when configuring SQL Server connection profiles:
Use a read-only user account with minimal privileges such as SELECT and VIEW DEFINITION. Avoid using the
saaccount or other system-level accounts for validation.Store credentials securely in a vault, Azure Key Vault, or a secrets manager. Do not hardcode credentials in configuration files or scripts.
Enable encrypted connections by including
encrypt=truein the JDBC connection URL for all production environments.Set
trustServerCertificate=falsein production to ensure proper certificate validation. UsetrustServerCertificate=trueonly in development environments with self-signed certificates.Rotate passwords periodically and update connection profiles accordingly.
Ensure SQL Server allows remote connections by verifying the configuration in SQL Server Configuration Manager and checking that firewall rules permit inbound connections on port 1433.
Use the
applicationNameparameter to identify Validata connections in SQL Server monitoring tools and logs.