Building pipelines from Snowflake
You can read from Snowflake as follows, and write to any target supported by Striim. Typically, you will set up data pipelines that read from Snowflake in two phases—initial load, followed by continuous replication—as explained in this concept article on Pipelines.
For initial load, you can use Database Reader to create a point-in-time copy of the existing source Snowflake dataset at the target, as described in Snowflake initial load.
After initial load has completed, you can start continuous replication by continuously reading the new data created in the same Snowflake dataset after the initial load was started, and then writing this new source data to the target.
For real-time continuous replication of new source data using CDC, you can use Snowflake Reader (see Snowflake continuous real-time replication using CDC).
If you choose not to enable CDC on Snowflake, you can use Incremental Batch Reader to read the new source data at regular intervals, allowing for continuous updates in near real time (see Snowflake continuous incremental replication). Incremental Batch Reader differs from Snowflake Reader in several ways, including not capturing DELETE operations at the source (see Differences between real-time and incremental replication).
Before building a pipeline, you must complete the steps described in Snowflake initial setup.
Striim does not have automatic pipeline wizards for Snowflake sources, so you must create separate applications for initial load and continuous replication, and after initial load completes, manually switch to continuous replication.
Before performing initial load, get the current timestamp as described in Switching from initial load to continuous replication of Snowflake sources.
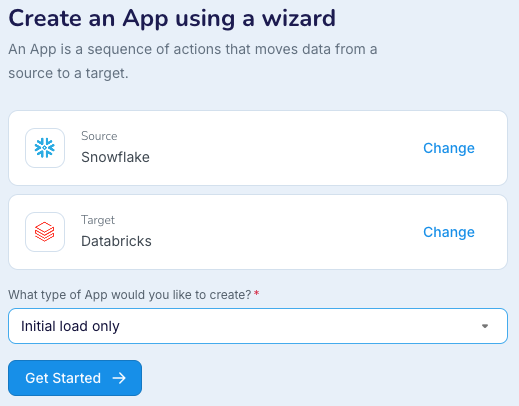
Create a schema and tables in the target and perform initial load: use a wizard with a Database Reader source and select Initial load only as the type of app to create.
Switch from initial load to continuous replication: see Switching from initial load to continuous replication of Snowflake sources.
Replicate new data: use a wizard with a Snowflake source (for continuous real-time replication) or an Incremental Batch Reader source (for continuous incremental replication) and select Change data capture only as the type of app to create.
Alternatively, instead of using wizards, you can create applications using Flow Designer, TQL, or Striim's REST API.